
Guide
What diamond criteria to favour ?
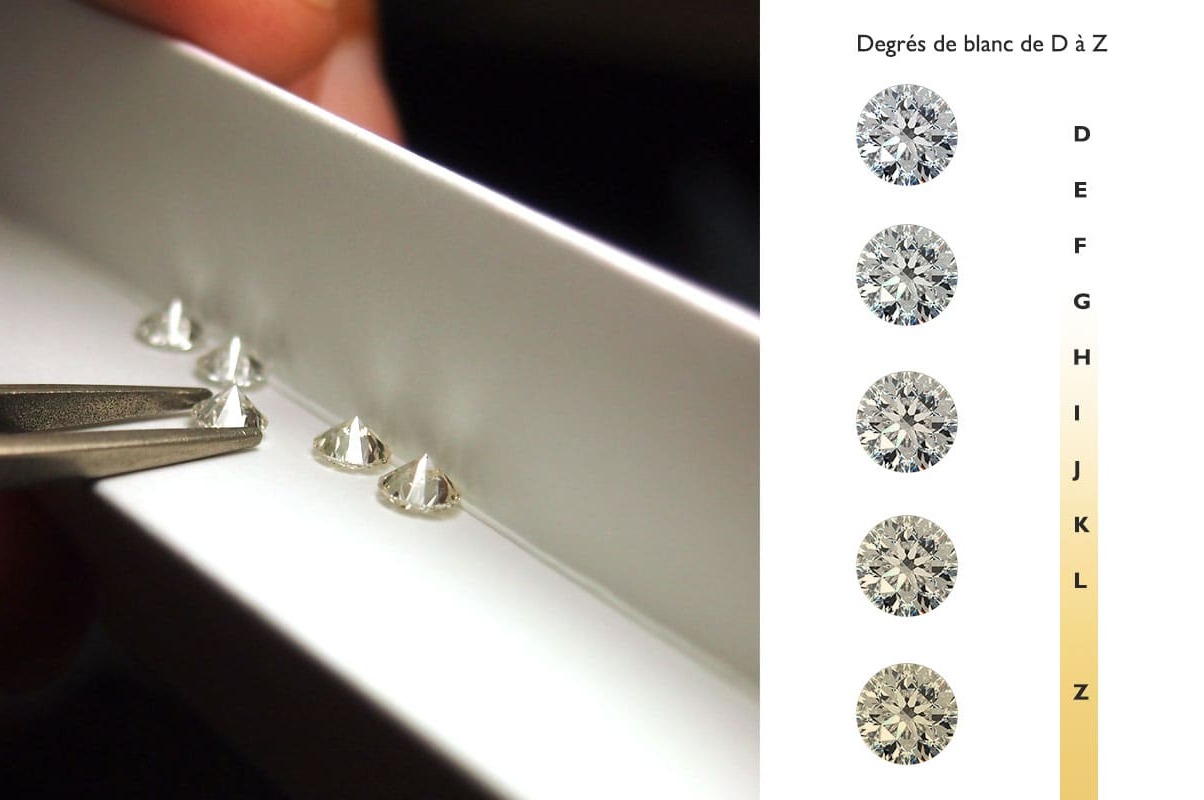


The vast majority of diamonds sold in jewelry have a color that varies from a perfect colorless to a slight hint of yellow. The degrees of white are graded on a scale from D (most colorless) to Z (most yellow-tinted). This information on the degree of white of a stone, which is very important when buying a diamond, is noted and indicated on the certificates of quality and authenticity issued by the GIA, HRD and IGI laboratories.
Diamond is a colorless stone sparkling with the thousand sparkles of the rainbow. Most of the time, natural diamonds are more or less white. The hues ranging from colorless to yellow give the definition of the color of the diamond. When the slightly yellow hue exceeds a certain threshold, the diamond is no longer considered white, but a fancy color diamond, i.e. a colored diamond. Color is one of the four "C's" that are used as criteria for the international standard for diamond grading: Carat (weight), Clarity, Cut, Color.
The most commonly used notation has been defined by the GIA, the Gemmological Institute of America, and is composed of letters from D to Z. The D is the most perfect value and the Z is the most yellow and therefore the worst on the white diamond scale.
These are the whitest diamonds. No color is perceptible to the eye of the specialist, from any angle. They are therefore considered colourless and therefore perfect and exceptional.
Almost as exceptional as the D's, E diamonds are colorless to the naked eye. It is necessary to use reference samples to determine whether the diamond is D or E color based on a very small hue that only a specialist can determine. As with D, E diamonds are among the whitest stones.
F diamonds are virtually colorless, but do not have the exceptional whiteness of D or E. A very slight yellowing is only detected at a certain angle by the eye of an expert. These are the diamonds that are most often used in fine jewelry.
As with F, the color of the stone is extremely faint and only perceptible from a certain angle by an expert. It is the first quality sold in beautiful traditional jewelry stores. To the naked eye, these diamonds appear colorless once cut and mounted on a piece of jewelry.
Ask for an independent and recognized certificate (GIA, HRD or IGI) attesting the quality of these rare whites.
Even if the color of H diamonds is not visible from the front, it is particularly clear when an expert looks at it from the side. The hue of yellow is still very faint, however, and is only really noticeable to the naked eye when compared to a superior diamond when mounted.
From diamonds I, the hue is visible from the front for the discerning eye. However, it is still weak enough to go unnoticed if the diamond is very well cut to give maximum brilliance to the stone.
These are very beautiful white diamonds (called "near colorless"), above the so-called "commercial" quality. Certificate always recommended for white diamonds greater than one carat.
J diamonds, like the I's, have a hue that is visible to the trained eye: J diamonds appear warmer and softer to the eye. The yellow hue can be counterbalanced by a setting on a yellow gold setting.
Lightly tinted diamonds are easily recognizable. The hue is visible to the untrained eye, even though the smaller ones still look white to an amateur. Diamonds of these colors still appear white to the naked eye to a non-professional if they are small (below 0.10 carat) but above 0.10 carat a color saturation occurs.
Tinted diamonds are very easily identifiable, the hue is immediately visible and clearly tends towards yellow. Their hue can be slightly attenuated on a yellow gold jewel, but the difference with a higher colored diamond will be easily detectable.

Engagement ring
4 Claws Classic
Solitaire diamond with 4 claws, a classic and timeless style. The highlighting of the diamond…

Ring
BRILLIANT
The perfect gift for your ever lasting love. Hand made french jewellery. Gold 750/000. Delivered in…

Pendant & Necklace
4 CLAWS
4 claw diamond pendant without bail. Forçat chain fixed by 2 rings on each side of the…

Wedding Band
RUBAN
Classic diamond wedding ring. 18 carats gold. Made in France. Delivered in a jewellery box. See…

Earrings
4 CLAWS CRADLE
Handmade diamond earrings, 4 claws heart-shaped cradle setting. Elegant exclusive design by…

Bracelet
ETERNITY
Diamond bezel bracelet. Very popular, a style that is both classic and contemporary. 18 carats…

Engagement ring
5 Claws Classic
Solitaire diamond with 5 claws. Solitaire offered in 18k white, yellow or pink gold (750/000) or in…

Ring
PRINCESS ROYAL
Style full of sparkle without being ostentatious. The dawn of passion and romance. Hand made to…

Pendant & Necklace
3 CLAWS B
Diamond pendant with 3 claws to enhance the stone as much as possible. Crimping carried out with…

Wedding Band
NOCEA
A modern style: diamonds are entwined in a crimped said "rail", a very contemporary…

Earrings
3 CLAWS PREMIUM
Handmade earrings with diamond belt based on mid height of the claws which are based on a rabbet.…

Bracelet
ERGO
Very modern, bright without being ostentatious. Pleasure of playing with the brilliance of…
The whiter a diamond is, the more sparkling it is. The purpose of a diamond is to sparkle. This is why as diamond dealers, we recommend that you be very demanding on this criterion, even if first of all, you must already make sure that you choose a diamond with a beautiful quality of cut (rated Excellent or Very Good by the GIA, HRD or IGI certificates). The whiteness of the diamond will enhance the brilliance of a well cut diamond, but it cannot compensate for the lack of life of a poorly cut stone. Finally, if you have to make a compromise between color and purity, we recommend that you give preference to the whiteness of the stone over its purity, as long as you do not go below SI2 purity, see SI1 for stones from 0.70 carat. Indeed the whiteness of a diamond is more easily seen with the naked eye than its purity, except if the impurities are very marked (stones called pitted: P1, P2, P3, P4, also called I1, I2, I3 and I4).
The choice of the color of the stone depends on the color of the metal on which the diamond will be set. The whiter the metal, such as white gold or platinum, the more colorless stones (D, E, F, G) will be ideal. A white metal will enhance the brilliance and whiteness of the diamond. Yellow gold, on the other hand, counterbalances the hue of a slightly yellow diamond by contrast. Once set on a jewel, mid-range diamonds (H, I, J) can therefore appear neutral if they are well cut (cut rated Excellent or Very Good by the GIA, HRD or IGI).
To better know which diamond color to choose, we invite you to read our article on Which diamond color to choose?
And to best combine these criteria of color and purity, we advise you to read our article What quality criteria should you choose for your diamond?
The color of the diamond can be natural or artificial. Mine diamonds have a natural hue ranging from colorless to brown. However, it is possible to change the color of these diamonds by different processes. There are also synthetic diamonds whose color can be fully customized.

Diamonds from the mines are of natural origin. They were created several million years ago in the Earth's mantle or during a collision with an asteroid: the carbon crystallized under heat and pressure and formed a gem. The purest diamonds contain only carbon, which refracts all colors and does not absorb any of them. However, carbon is not necessarily the only element present in the stone: it can also contain other elements that will have an impact on the color of the stone. The most common yellow hue is for example due to the presence of nitrogen, an element that slightly refracts the yellow color of the light spectrum.
A diamond can be treated to change its color, it is then called "color enhanced". Two of the techniques used are thermo-pressure (HTHP) and irradiation. The first one allows thanks to very high temperature and pressure to lighten the color of a diamond that is a little too yellow. The second technique is used to create stronger colors to bring the diamond into the category of colored diamonds. In order to be sure that the color of your diamond is natural, without any treatment, always buy a diamond certified by one of the 3 major laboratories: GIA, HRD and IGI. On the certificate, check that it does not mention any HTHP treatment or irradiation. If none of this is mentioned, the color of your diamond is natural.
Synthetic diamonds, or artificial diamonds, are created in the laboratory. It is then possible to create "perfect" diamonds by limiting the nitrogen inclusions that give the yellow hue. It is also possible to set the color of the diamond by adding inclusions of various elements such as nitrogen, ammonia or boron. It is also possible to make colors that do not exist in nature. In order to be sure that your diamond is of natural origin, and not synthetic, always buy a diamond certified by one of the 3 major laboratories: GIA, HRD and IGI. On the certificate, check that it is mentioned: "Natural Diamond".
To observe the color of a diamond, it is advisable to have rested eyes. It is not mandatory to use a magnifying glass, even if it is a welcome help and facilitates the observation of gems.
The only necessity is to pay attention to the light, and in particular to its temperature. It must correspond to 7000° kelvin, which is the equivalent of natural daylight in the northern direction. It must be limited in UV and blue radiation, it is better to avoid the mountains and the seaside in natural conditions, and neon lights indoors for example. The best choice is to use a cold light lamp, LED, which best reproduces natural light.
Another essential element is a white support, usually a white cardboard folded at 90°. The nuances of the diamond appear when viewed from all angles.
It is not obvious to see with the naked eye the degree of hue of white diamonds. In addition to observing it on a white surface, it is often necessary to compare it to others to determine its exact hue. The most common is to use a comparative method using a set of control stones corresponding to the conventional scale. A control diamond is placed next to the diamond to be identified. When the control is at the limit of its value, it is sufficient to go up or down the scale according to the difference observed until an equivalence is obtained.
The more colorless the diamond is, the greater its value and the more expensive it is. For lightly colored diamonds, the price can vary from single to double depending on the degree of hue. The more yellow the diamond is, the more it loses value, even if the color is less noticeable after cutting and once the stone is set on a piece of jewelry.
A fancy color diamond is a diamond that is outside of the previously mentioned nomenclature. In fact, there are diamonds of all colors, especially in the continuity of the hue of white diamonds. These diamonds have a clear color ranging from yellow to brown and due to nitrogen inclusions in their structure.
Beyond the Z range, there are six steps from lightest to darkest according to the GIA: Fancy, Light Fancy, Intense Fancy, Vivid Fancy, Deep Fancy Dark. From Fancy Light to Fancy Vivid, the colors are more or less intense on the same color: yellow. Fancy Deep and Fancy Dark correspond to the brown color that a natural diamond can also commonly have.
Except for the exceptional and historic colored diamonds that break records in the auction room, the value of colored diamonds varies depending on the hue. Fancy diamonds are worth less than a white diamond, although some hues are sought after and rare. In general, brown and yellow diamonds are the most common diamonds found in nature, but they are also the least expensive and least sought after in jewelry.
French jewellery
Our slogan
Passion, Authenticity, Expertise
Certified diamonds
By 3 world-renowned laboratories


Exceptional quality of stone and jewel

Customer service at your service, provided by diamond dealers
Sealed diamonds with a certificate of quality and authenticity
French manufacturing

30-Day « satisfied or reimbursed »
guarantee

Online secured payment
De Hantsetters, diamonteers since 1888
Customer service at your service, provided by diamond dealers
All our diamonds are independently certified by 3 world-renowed organisations


Want to talk to a diamonteer ?
Contact us nowWe recommend the following 5 selections
To help you choose, we recommend 5 categories of diamonds that correspond to different purposes: Volume (maximizing weight), Balance (compromise weight and quality), Perfection (maximizing quality), Cut of heart (the i-diamonds recommendation), Promotion (one-time price offer).

Volume effectmaximize the weight of the diamond relative to its price, I-J color and SI1-SI2 clarity

Choice of balancefavor a good balance of color / clarity: F-G / VS1-VS2

Perfectionmaximize the quality of the diamond with the best criteria of color and clarity: D IF

Favorite's choicediamond selected by i-diamants for its shine, D-E color, VS1 clarity, cut criteria all rated

Promotionsdiamond with a 5% promotion
Carats / Diamond weight
Move the diamond weight slider and view the rendering on a hand, chest or ears.
Carat
mm (Approx.)
0,30 Ct
4,30 mm
0,40 Ct
4,60 mm
0,50 Ct
5,00 mm
0,70 Ct
5,70 mm
1,00 Ct
6,30 mm
1,25 Ct
6,90 mm
1,50 Ct
7,30 mm
Equivalence for round brilliant diamonds
Examples of different diamond measures

0,30 Ct

0,50 Ct

0,80 Ct

1,00 Ct

1,50 Ct
Diamond colours
Our recommandation
We recommend diamonds with a white hue between D (exceptional white+) and H (white) because the whiteness of the diamond increases its brilliance. From color grade I and J (slightly tinted) onwards, diamonds are slightly yellow-tinted: avoid on white gold and acceptable on yellow gold.
D-EExceptional white
F-GExtra white
HWhite
I-JSlightly tinted
K-MTinted white
N-ZVery tinted

Diamond clarity
Our recommandation
We recommend that you avoid choosing a Pique diamond, because inclusions are easily seen with the naked eye, alter the brilliance and can even weaken the stone. The clarities included in VS and SI1 are the most recommended , unless you have the budget to let yourself be tempted by IF or VVS clarities, which sign the diamond in its highest dimension: that of purity.
IFPure
VVSVery very small inclusion(s)
VSVery small inclusion(s)
SISmall inclusion(s)
PIncluded

IF : Pure
No inclusion inside the stone
VVS1 VVS2 : Very very small inclusion(s)
Very difficult to see with a 10X magnifying glass
VS1 VS2 : Very small inclusion(s)
Difficult to see with a 10X magnifying glass
SI1 SI2 : Small inclusion(s)
Easy to see with a 10X magnifying glass and difficult to see with naked eye
P1 P2 P3 : Included
Easy to see with naked eye
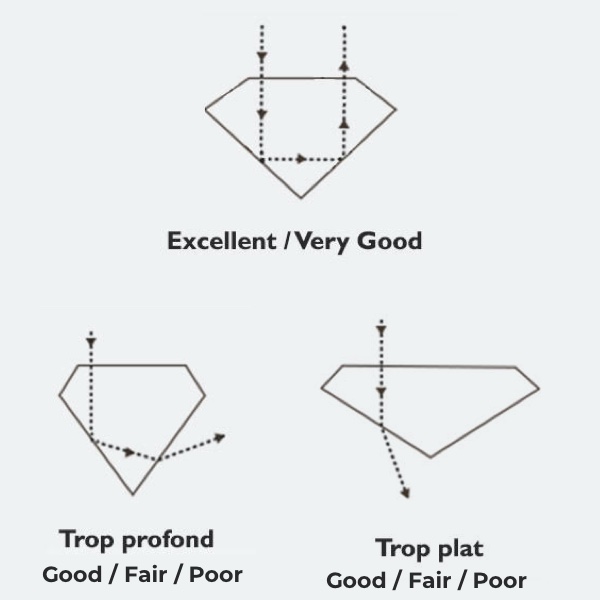
Diamond cut
When a diamond is well cut, light reflects from one facet to the other, making the most of the diamond's high refractive property. A less well-cut diamond lets some of the light escape.
Our recommandation
We advise you to choose a diamond with a quality rating equal to Excellent (EX) or Very Good (VG) to maximize the refraction of light and therefore the diamond brilliance.
EXExcellent
VGVery Good
GGood
FFair
PPoor
Most recognized certificates: GIA, HRD and IGI
Always ask to see the certificate before purchasing a certified diamond. For all of our certified diamonds, we display a link (GIA, HRD or IGI) that you can click to view the diamond’s full certificate.
We only offer natural diamonds accompanied by a certificate of authenticity and quality issued by one of the 3 most prestigious and world-renowned laboratories: GIA, HRD and IGI. The certificate number is engraved on the girdle (circumference) of all our HRD, IGI and GIA certified diamonds.



Laser engraving
The three major diamond certification laboratories HRD, IGI and GIA laser engrave the certificate number on the girdle (circumference) of the diamond. The certificate number is therefore engraved on all our HRD, IGI and GIA certified diamonds. This is a proof of the good match of the diamond and its certificate. The inscription is very small (to preserve the purity of the stone) and very difficult to read with the magnifying glass 10X.

If you order only the diamond (without the jewel), it will be delivered under seal in a rigid plastic pouch (see photo below) for diamonds certified by HRD or by IGI. For GIA diamonds, the seal must be specifically requested in the comments field during the ordering process.
Diamond Fluorescence
Fluorescence is a luminous effect that some diamonds exhibit when exposed to ultraviolet light. They show visible light, usually blue.
Our recommandation
Since fluorescence may in some cases give a milky diamond appearance, prefer a diamond without fluorescence ("None" or "Nil")

None or Nil
Absence of fluorescence
Slight or Faint
Little fluorescence
Medium
Medium fluorescence
Strong
Strong fluorescence
Very Strong
Very strong fluorescence
Diamond Polishing
When cutting the diamond, each facet must be polished. If a diamond has no scratches or very minor scratches on the surface, the polish is high. The better the polishing, the more it allows the transmission of light through the different facets of the diamond.
Our recommandation
We recommend choosing a polish rated Excellent (EX) or Very Good (VG) to ensure the best finish and shine.
EXExcellent
VGVery Good
GGood
FFair
PPoor
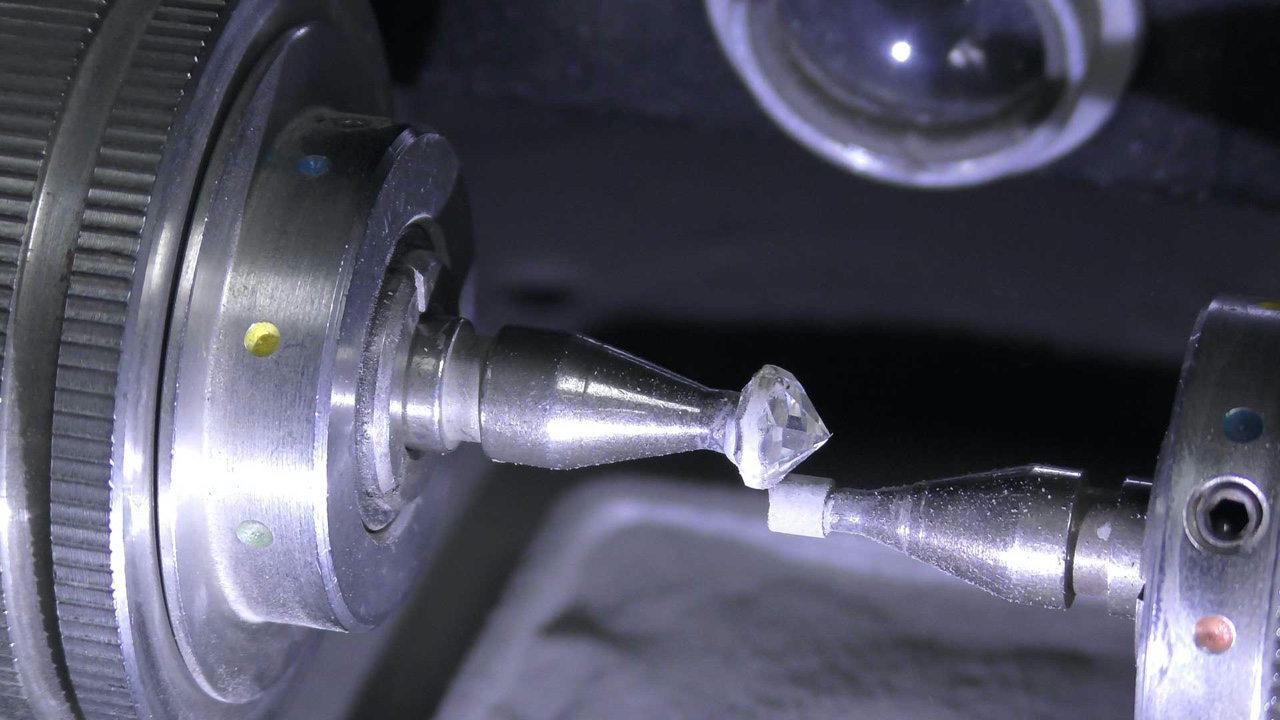

Diamond Symmetry
Symmetry describes the symmetrical accuracy of the facets of the diamond in terms of dimensions and angles, as well as the centering of the table and the centering of the breech point of the diamond. A higher level of symmetry creates optimal shine and scintillation.
Our recommandation
We advise you to choose a diamond with a symmetry rating equal to Excellent (EX) or Very Good (VG) to maximize the sparkle.
EXExcellent
VGVery Good
GGood
FFair
PPoor

As you continue your navigation, you accept the use of cookies to provide our service and to secure transactions on our website.
Don't show anymore More info